All living beings reproduce. In fact, reproduction is one of the living function, a process to produce new organisms. So, plants reproduce too. Plants can undergo two kinds of reproduction: asexual and sexual.
Asexual reproduction involves one parent only. When plants reproduce asexually they do not produce gametes, the reproductive cells. On the contrary, to reproduce sexually plants produce gametes and have male and female reproductive organs in their flowers or other reproductive structure in plants without them, like mosses and ferns.
Plants can reproduce asexually by:
Spores. They are special cells formed in organs called sporangia.
Buds. They are structures that can be found on underground or overground roots and stems.
Fragmentation. A new plant is created from a fragment of the parent plant.
Sexual reproduction comprises several stages:
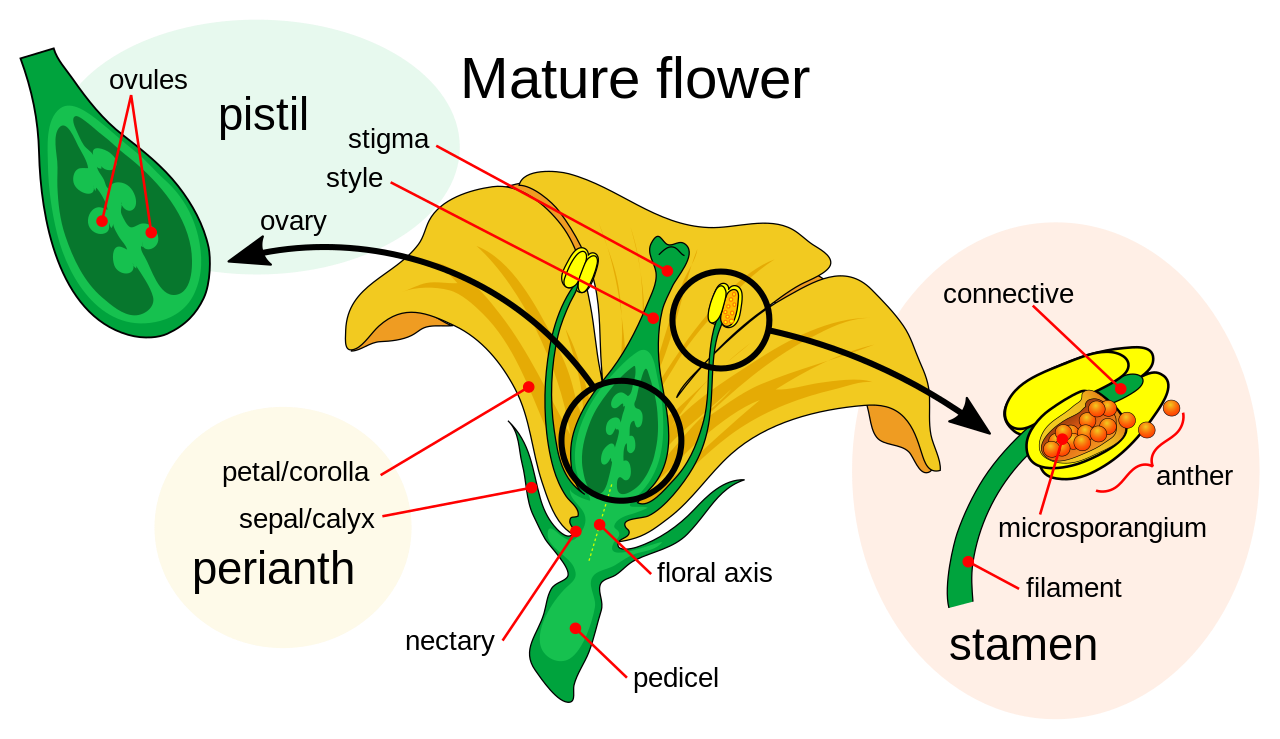
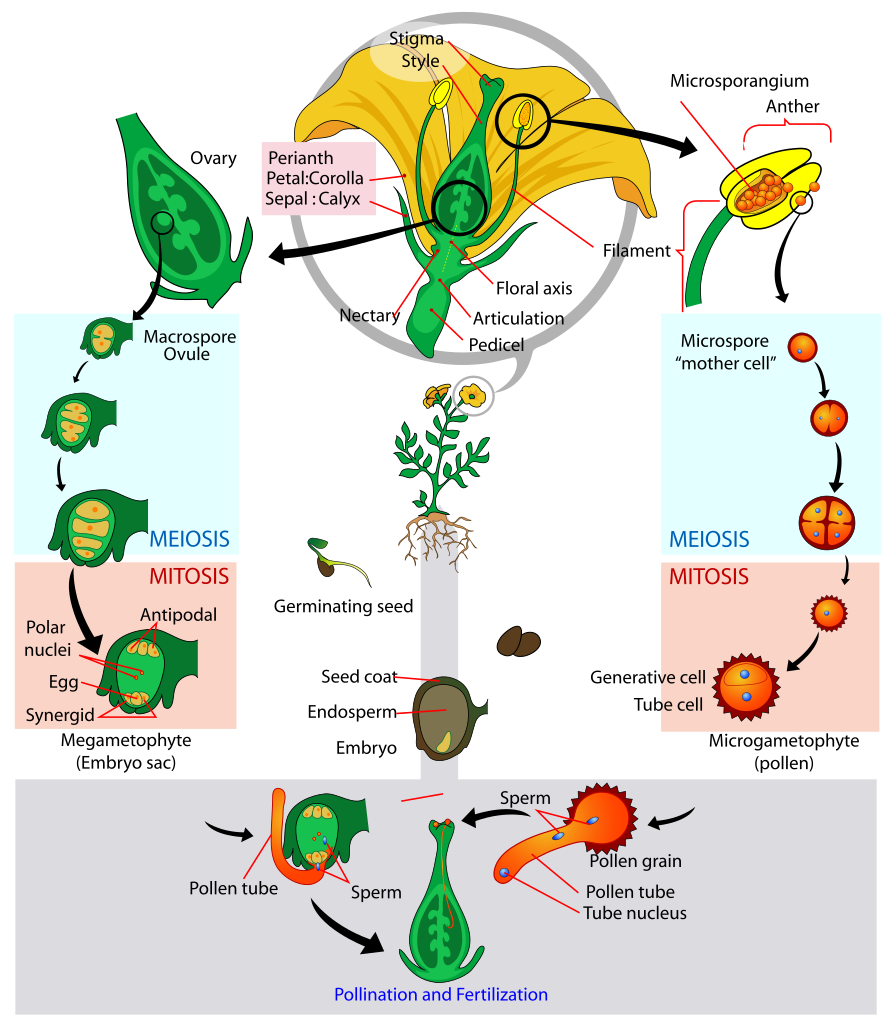 1. The formation of gametes. They are formed in flowers. Flowers are made of modified leaves. They have stamens, the organs where the grains of pollen are formed, and the pistil, where the female gametes are.
1. The formation of gametes. They are formed in flowers. Flowers are made of modified leaves. They have stamens, the organs where the grains of pollen are formed, and the pistil, where the female gametes are.
2. Pollination. Grains of pollen are carried from the anthers, in the stamens, to the stigma of the pistil. Depending on how the grains of pollen are transported pollination can be classified as either entomophilous, carried out by insects, or anemophilous, by the wind.
3. Fertilization. The male and female gamete join to form a zygote.
4. Seed formation. The zygote develops and the seed forms.
5. Fruit formation and seed dispersal. In platns with flowers, a fruit form around the seed.
6. Seed germination. When the seed falls to the ground, it absorbs water, opens and the embryo begins to grow. The root appears and sinks into the soil, and the stem al leaves appear and grow towards the light.
Some plants alternate their type of reproduction. Asexual reproduction, via spores, alternates with sexual reproduction, through gametes. Sexual reproduction creates a plant called sporophyte and sexual reproduction, via spores, creates a plant called gametophyte.
Activities:
1. Working with vocabulary
Translate to Spanish the following words: gamete, moss, fern, spore, bud, root, stem, leaf, stamen, pistil, entomophilous, anemophilous, seed.
2. Draw a picture of a flower and label its parts. If you want, you can send me a picture of your drawing by e mail.
3. Where are the male and female gametes formed in plants?
4. What is the difference between entomophilous and anemophilous pollination?
JULIA CABALLERO REYES 1ESO A.
ResponderEliminar1.
Gamete: Gameto
Moss: Musgo
Fern: Helecho
Spore: Espora
Bud: Germinar
Root: Raíz
Stem:Tallo
Leaf: Hoja
Stamen: Estambre
Pistil: Pistilo
Entomophilous: Entomófilo
Anemophilous: Anemófilo
Seed: Semilla
3.
In the flowers and they are in the stamen.
4.
In entomophilous, carried out by insects, but in anemophilous, by the wind.
1. Working with vocabulary
ResponderEliminarTranslate to Spanish the following words: gamete, moss, fern, spore, bud, root, stem, leaf, stamen, pistil, entomophilous, anemophilous, seed.
Gameto, musgo, helecho, espora, brote, raíz, tallo, hoja, estambre, pistilo, entomófilo, anemófilo, semilla.
2. Draw a picture of a flower and label its parts. If you want, you can send me a picture of your drawing by e mail.
In the email.
3. Where are the male and female gametes formed in plants?
In the ovary and at the tip of the stamen filament.
4. What is the difference between entomophilous and anemophilous pollination?
That the anemophilia transports its pollen through the wind and the entomophyll needs an insect to transport the polem.
HOLA, SOY CARMEN / 1º ESO A
ResponderEliminar1: Gametos, Musgo, Helecho, Espora, Yema, Raíz, Vástago, Hoja, Estambre, Pistilo, Entomófiloso, Anemofílico, Semilla
2: Email
3: Female1: Pistil
Male1: Anthers
4: Depending on how the grains of pollen are transported they can be either entomophilous or anemophilous.
Por favor, poned vuestros nombres en las colaboraciones.Si no es imposible que pueda saber quiénes sóis.
ResponderEliminarVicente Maroto Padial
ResponderEliminar1. gameto, musgo, helecho, espora, brote, raiz, tallo, hoja, estambre, pistilo, entomófilo, anemófilo, semilla
2. I send it by email
3. Pistil: female gametes; Anters: male gameters
4. Depending on how the grains of pollen are transported pollination can be classified as either entomophilous, carried out by insects, or anemophilous, by the wind.